PVB laminated glass is engineered to offer superior safety, acoustic insulation, and design flexibility, and its performance is highly influenced by thickness and weight. From residential windows and commercial facades to automotive windshields and high-security environments, the correct specification of laminated glass dimensions ensures optimal structural strength and user protection. In this article, we provide a comprehensive guide to understanding PVB laminated glass thicknesses, how weight is calculated, and what factors influence your choice of configuration based on use case and safety standards.
What Is PVB Laminated Glass and Why Thickness Matters
PVB laminated glass is constructed by bonding two or more glass sheets with a polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer under heat and pressure. The PVB interlayer plays a critical role in impact absorption, sound reduction, and glass adhesion. When the glass breaks, the interlayer holds the fragments together, preventing dangerous shattering and maintaining partial structural integrity.
The overall performance of laminated glass—whether for strength, acoustics, or energy efficiency—is significantly influenced by its thickness. Thicker laminated glass panels are more resistant to impact, flexing, and environmental conditions, while thinner ones may be suitable for interior partitions or lightweight installations.
To explore how this material is fabricated, visit How PVB Laminated Glass Is Manufactured?.
Standard Thickness Configurations for PVB Laminated Glass
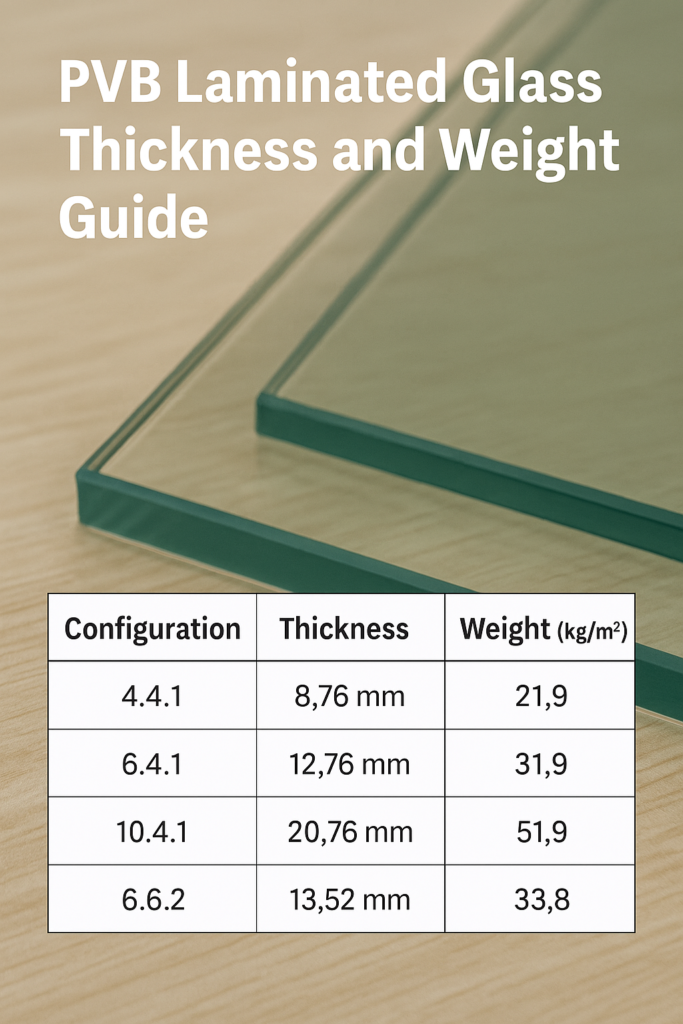
Laminated glass thickness is typically expressed in the format of glass + interlayer + glass (e.g., 4.4.1, 6.4.2, 10.8.4), where the numbers represent millimeters.
Here are the most common standard configurations:
- 4.4.1 (approx. 8.76 mm total): Two 4 mm glass sheets + 0.76 mm PVB
- 6.4.1 (approx. 12.76 mm): Two 6 mm sheets + 0.76 mm PVB
- 10.4.1 (approx. 20.76 mm): Two 10 mm sheets + 0.76 mm PVB
- 5.5.2 (approx. 11.52 mm): Two 5 mm sheets + 1.52 mm PVB
- 6.6.2 (approx. 13.52 mm): Two 6 mm sheets + 1.52 mm PVB
Thicker PVB interlayers like 1.52 mm (double thickness) are often used for high-security, acoustic, or hurricane-rated glass. For design-specific variants such as frosted or colored interlayers, the configuration may change slightly to accommodate extra material.
To explore the role of interlayer variations, check PVB Laminated Glass: Common Interlayer Types.
Weight Calculation of PVB Laminated Glass
To calculate the weight of a laminated glass panel, the following formula is typically used:
Weight (kg/m²) = Glass thickness (mm) × 2.5
This assumes the density of glass is approximately 2.5 grams/cm³. For laminated glass, you need to account for the thickness of both glass panes and the PVB interlayer.
Example Weights:
- 4.4.1 (8.76 mm):
8.76 mm × 2.5 = 21.9 kg/m² - 6.4.1 (12.76 mm):
12.76 mm × 2.5 = 31.9 kg/m² - 10.4.1 (20.76 mm):
20.76 mm × 2.5 = 51.9 kg/m²
Heavier laminated glass requires stronger framing systems and more robust handling equipment, particularly for high-rise applications or overhead glazing.
Factors That Influence Thickness Selection
The ideal PVB laminated glass thickness is determined by the following factors:
1. Safety Requirements
Thicker laminated glass is recommended for areas subject to heavy impact, including:
- Doors and storefronts
- School and hospital windows
- Balconies and balustrades
- Vehicle windshields (automotive standard = 6.76 mm or more)
Learn more in PVB Laminated Glass: Automotive Safety.
2. Acoustic Performance
Soundproofing requires thicker glass and/or acoustic interlayers. Laminated glass with 6.6.2 or thicker is often used in:
- Hotels and residential towers
- Recording studios and hospitals
- Offices in urban or industrial zones
3. Structural Load and Wind Pressure
The glass panel’s ability to withstand wind load depends on panel size, thickness, and installation conditions. For large glass curtain walls or external glazing, panels may exceed 20 mm in total thickness.
4. Aesthetic and Design Goals
Where transparency and lightness are priorities—such as in interior partitions or decorative panels—thinner glass may be used, such as 3.3.1 or 4.4.1. However, even these configurations provide higher safety than monolithic glass.
5. Security and Intrusion Resistance
Laminated glass with multiple PVB layers (e.g., 3.04 mm or more) is used for:
- Bank counters and ATMs
- Embassies and government buildings
- High-risk commercial storefronts
PVB Laminated Glass Installation Considerations
The weight and thickness of laminated glass panels significantly impact the installation process. Best practices include:
- Using cranes or suction lifters for large or heavy panels
- Ensuring frame support systems are engineered to withstand panel weight
- Allowing sufficient edge clearance for thermal expansion
- Sealing edges to prevent delamination from moisture intrusion
For panels installed overhead or in frameless glass railings, the correct thickness ensures compliance with building codes and occupant safety.
PVB Laminated Glass Maintenance Based on Thickness
While the basic PVB laminated glass care practices remain consistent—such as cleaning with pH-neutral solutions and inspecting for edge damage—thicker glass may need:
- Structural inspections for deflection
- Sealant checks to ensure edge bonding integrity
- Frame integrity checks to prevent sagging or panel shifting over time
Maintenance frequency often increases with thickness due to weight-induced stress on fittings and hardware, especially in outdoor applications.
Cost Implications of Laminated Glass Thickness
The price of PVB laminated glass increases with both glass and interlayer thickness. While thinner panels such as 4.4.1 may range between $20–$30/m², thicker glass like 10.8.4 may exceed $80/m² or more, depending on the configuration and application.
Other cost factors include:
- Interlayer type (acoustic, solar control, colored, etc.)
- Panel dimensions and cut complexity
- Certification requirements (e.g., hurricane-rated, bullet-resistant)
- Installation logistics and freight
Purchasing from reputable PVB laminated glass manufacturers ensures accurate weight data, compliance with regional thickness standards, and delivery of safety-certified products.
Conclusion: Matching Glass Thickness to Function and Code
Selecting the correct PVB laminated glass thickness ensures that the material performs as expected under real-world conditions—whether that means protecting vehicle occupants, enhancing acoustic comfort in a hotel room, or withstanding strong wind forces on a high-rise.
From standard architectural use to specialty applications like structural glazing or security barriers, understanding laminated glass weight and thickness helps in:
- Accurate design planning
- Cost estimation
- Installation execution
- Regulatory compliance
Choosing the right thickness also prevents overengineering, keeping projects both safe and economically efficient. As laminated glass technology evolves, customization of thickness and interlayers will continue to align performance with creative vision.
To dive deeper into the applications and options available, explore: