Discover how laminated glass prevents injury and improves building safety. Avoid issues like composition imbalance, inconsistent lighting, and flat perspective with this high-performance safety glass.
In construction and design, safety is as important as style. One material that excels in both areas is laminated glass. Commonly used in modern architecture, vehicles, and even interior applications, laminated glass is designed to reduce injury risk during impact or breakage. But how exactly does it work?
This guide breaks down how laminated glass prevents injury, how it differs from other safety glass types, and why it’s the preferred choice for both commercial and residential projects.
What Is Laminated Glass?
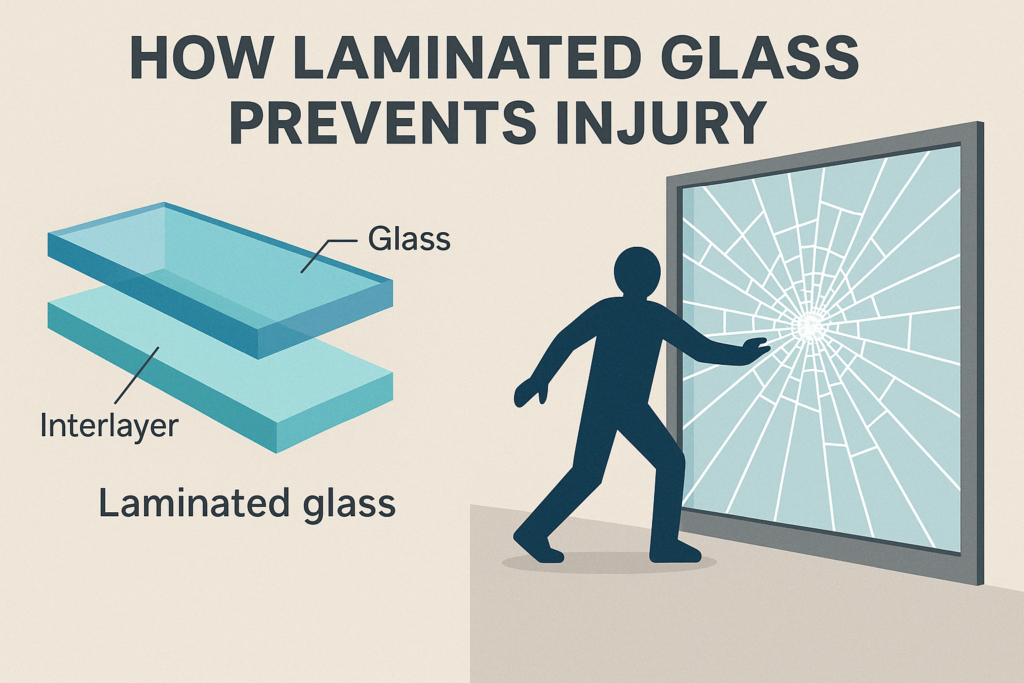
Laminated glass, also referred to as glass laminated, is a type of safety glass made by bonding two or more layers of glass with a flexible interlayer, usually polyvinyl butyral (PVB) or ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA).
When laminated glass breaks, the interlayer holds the fragments in place, preventing them from scattering and causing injury. Unlike regular or tempered glass, which can shatter into sharp or airborne pieces, laminated glass remains mostly intact.
🔗 Learn more: laminated glass
How Laminated Glass Prevents Injury
1. Shatter Control
Upon impact, laminated glass may crack, but it doesn’t break apart. The interlayer absorbs shock and holds the broken pieces together. This reduces the risk of:
- Lacerations from sharp shards
- Falling glass in overhead installations
- Flying fragments during accidents or explosions
2. Impact Resistance
The layered structure acts like a cushion, making it far more resistant to blunt force. In car accidents, for instance, laminated windshields don’t cave in easily and prevent passengers from being ejected or injured by flying debris.
3. Post-Breakage Stability
Even after cracking, laminated glass remains stable within its frame, offering:
- Continuous protection
- Time for evacuation in emergencies
- Reduced risk of collapse in structural glazing
Where Injury-Prevention Matters Most
Laminated safety glass is often used in areas where human safety is a top priority:
- Automobiles: Standard in windshields
- High-rise buildings: Overhead glazing, skylights, curtain walls
- Balconies and stair railings: Prevent accidental falls and glass failure
- School buildings and hospitals: Minimize injury risk for vulnerable groups
- Public transit systems: Buses, trains, airports
Common Use Cases of Laminated Glass
Exterior Applications
- Windows and doors in hurricane zones
- Canopies and skylights
- Glass facades and storefronts
Interior Applications
- Glass partitions and room dividers
- Stair balustrades and flooring
- Soundproof walls in studios or meeting rooms
These applications also address visual design concerns like composition imbalance, inconsistent lighting, and flat perspective by offering clarity, reflection control, and uniformity across large installations.
Laminated Glass vs Other Glass Types
| Feature | Laminated Glass | Tempered Glass | Float Glass |
|---|---|---|---|
| Breakage Pattern | Cracks but stays intact | Shatters into blunt pieces | Shatters into sharp shards |
| Injury Prevention | Excellent | Moderate | Poor |
| Post-Break Safety | High | None | None |
| Sound Insulation | Good | Low | Low |
| UV Protection | Yes | No | No |
| Cost | Higher | Moderate | Low |
How Laminated Glass Enhances Building Design
Using glass laminated panels not only increases safety but also improves building performance and design aesthetics:
- Consistent lighting: Laminated glass can reduce glare and diffuse sunlight
- Depth and clarity: Avoids a flat perspective in all-glass walls
- Material balance: Matches other components visually for a clean, modern look
Custom interlayers are available in:
- Tinted colors
- Frosted or patterned styles
- Digital prints and branding
Laminated Glass Price Breakdown
The price of laminated glass varies depending on:
- Thickness (e.g., 6.38mm, 10.76mm, 13.14mm)
- Type of interlayer (standard, acoustic, colored)
- Size and shape
- Quantity ordered
General Price Ranges:
- Standard laminated glass: $20–$35/m²
- Acoustic laminated glass: $40–$60/m²
- Decorative laminated panels: $50–$80/m²
Contact certified laminated glass manufacturers for accurate pricing tailored to your needs.
Related Search Keywords to Target
- what is laminated glass used for
- safety laminated glass panels
- laminated glass manufacturers near me
- laminated glass price per square foot
- best glass for injury prevention
- laminated vs tempered glass safety
- laminated glass for stairs and balconies
- custom laminated glass panels
- UV laminated glass
- laminated glass specifications
Why Choose Laminated Glass for Safety?
If your goal is injury prevention, no other glass type offers the same level of protection. Whether you’re a builder, architect, or homeowner, choosing laminated glass is a long-term investment in both safety and aesthetics.
It provides:
- Physical safety
- Noise control
- UV protection
- Design flexibility
And most importantly — peace of mind.
Final Thoughts
Laminated glass is engineered to protect people from harm without compromising design integrity. Its ability to prevent injury during impact makes it indispensable in today’s safety-conscious architecture. From homes and cars to skyscrapers and schools, laminated glass is shaping safer, smarter spaces.
🔗 Dive deeper: laminated glass