This guide explains how low emissivity glass balances daylight and solar control, what design choices affect performance, and how to specify it intelligently
low emissivity glass isn’t just a nicer window upgrade. It’s a practical, proven tool for reducing the environmental footprint of buildings
This guide breaks down the main factors that affect low emissivity glass pricing today, so you can understand where the money goes and how to specify smartly
we’ll explore how low emissivity glass works inside insulated glass units (IGUs), why it outperforms standard clear double glazing, and when upgrading to Low-E
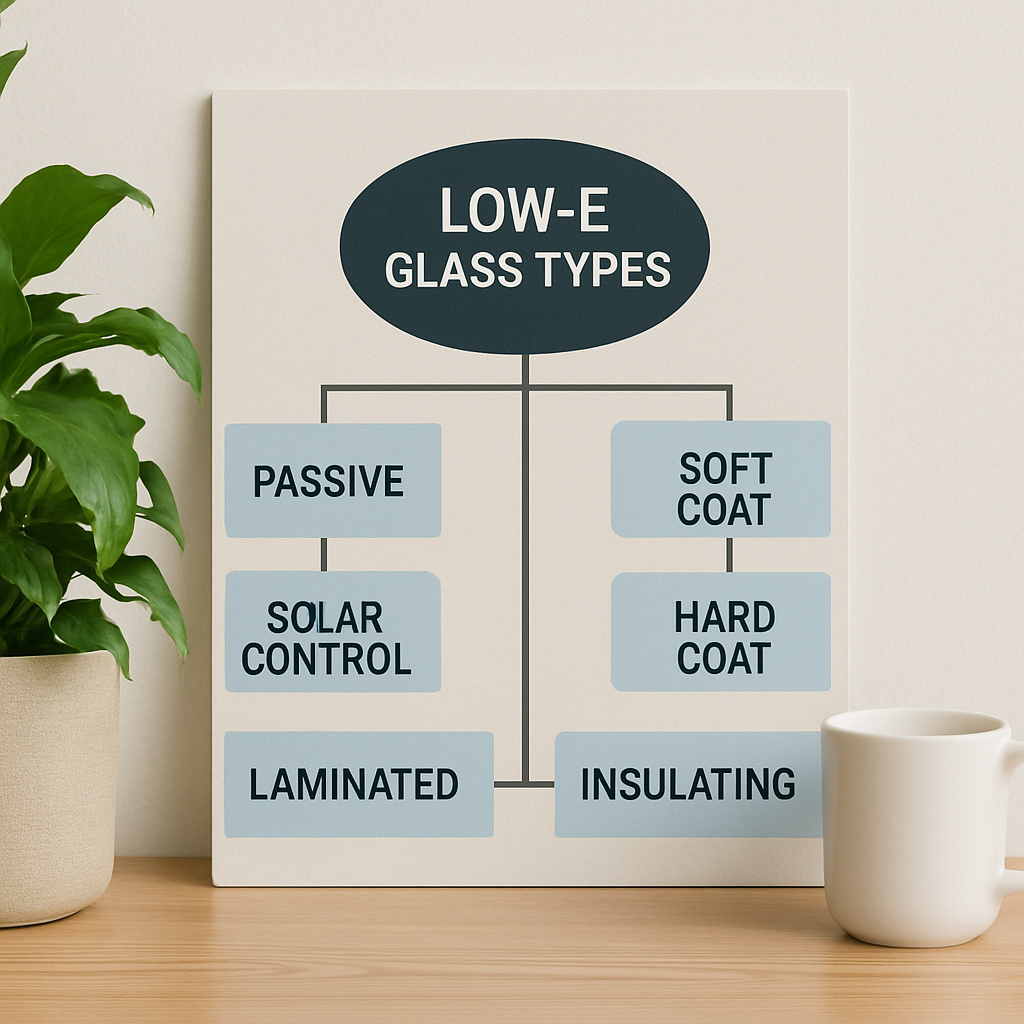
This guide explains what makes low emissivity glass different from tinted and reflective glass, how each type controls heat and light
we’ll explore why low emissivity glass is superior to standard clear glass, and when upgrading from clear to Low-E makes the biggest difference
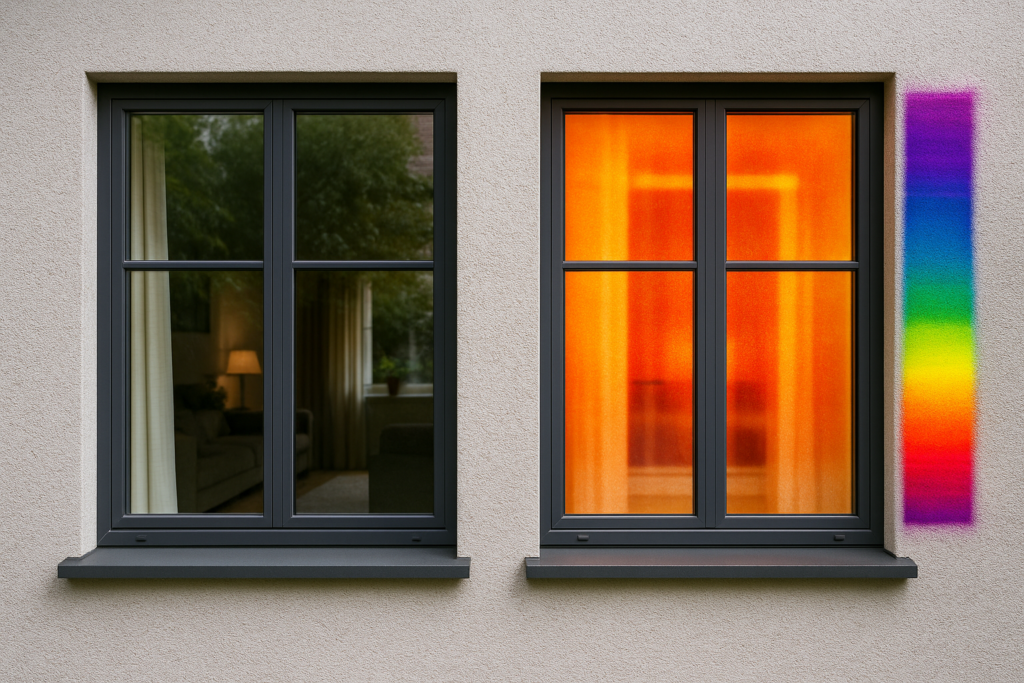
we’ll break down how low emissivity glass helps control heat in hot climates, how it works with the solar spectrum, and where it should be used
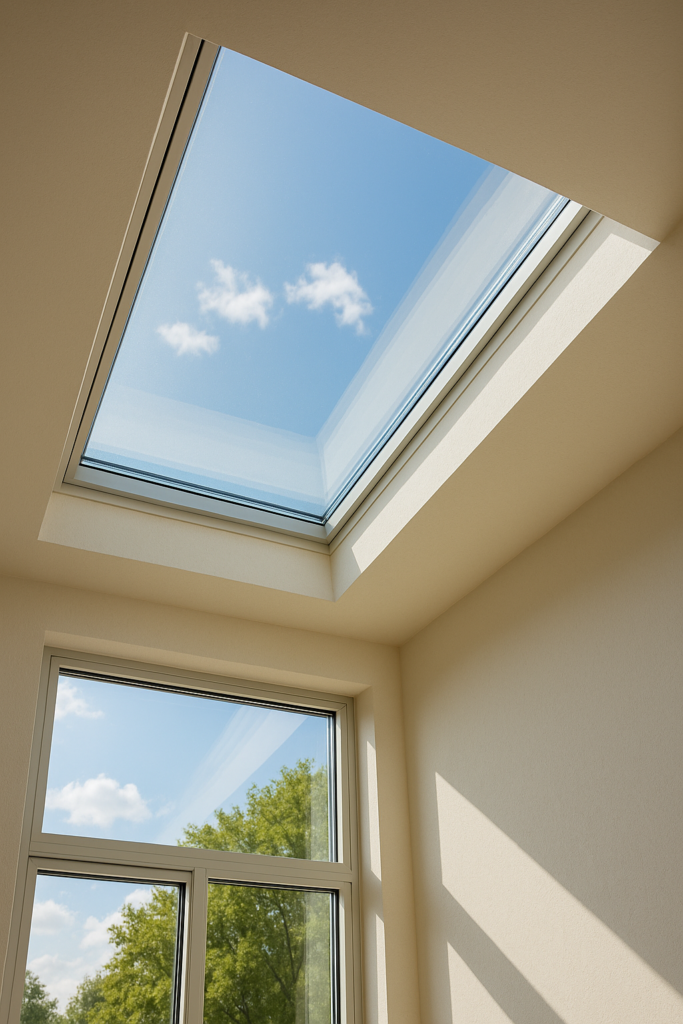
we’ll look at where low emissivity glass works best in skylight designs, how to match it to climate and orientation, and how to combine it with framing, shading
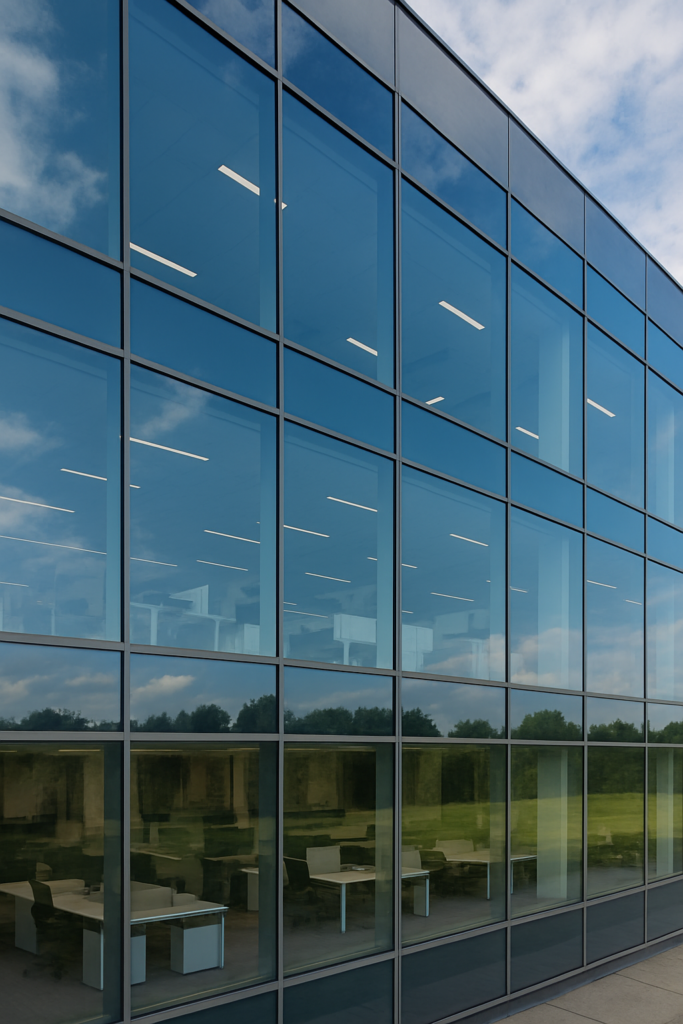
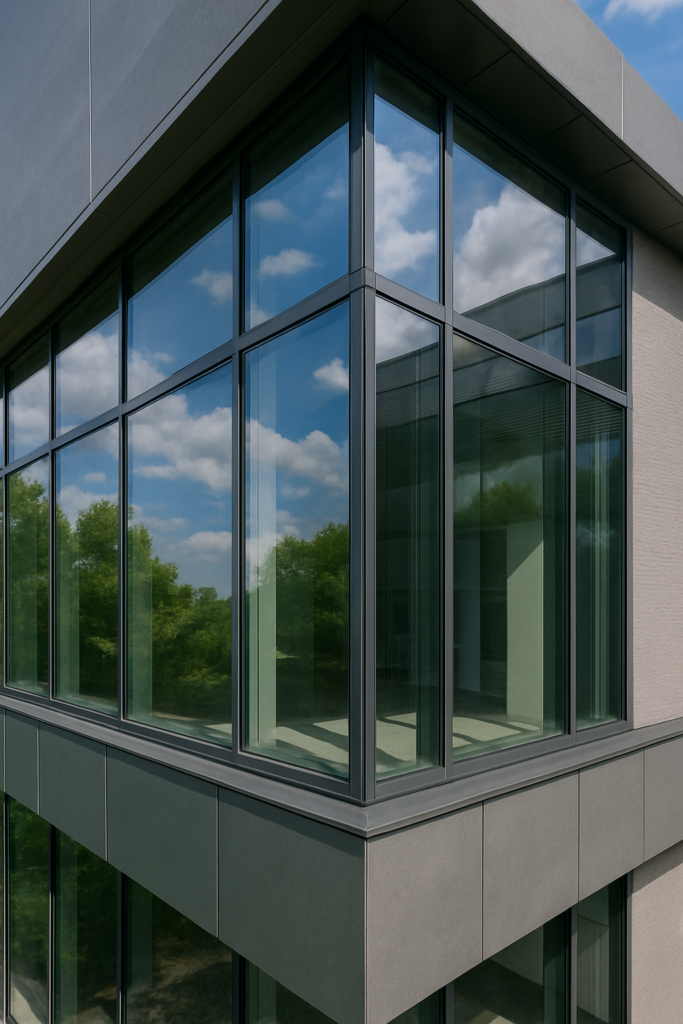
we’ll explore why commercial facades prefer low emissivity glass solutions, and how they deliver value across performance, comfort, design, and long-term cost.
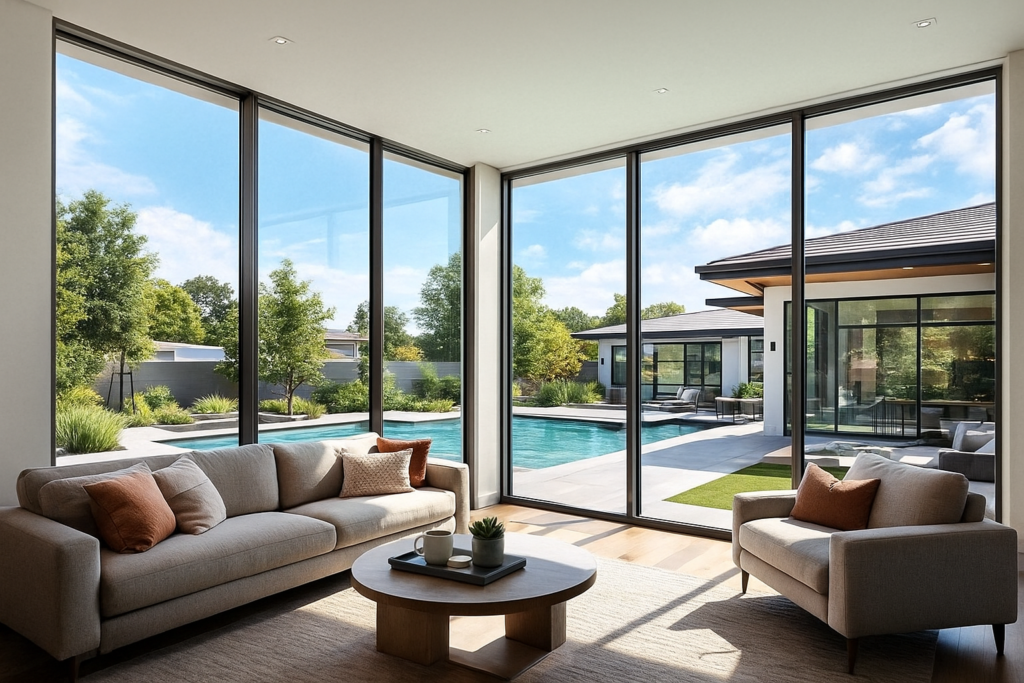
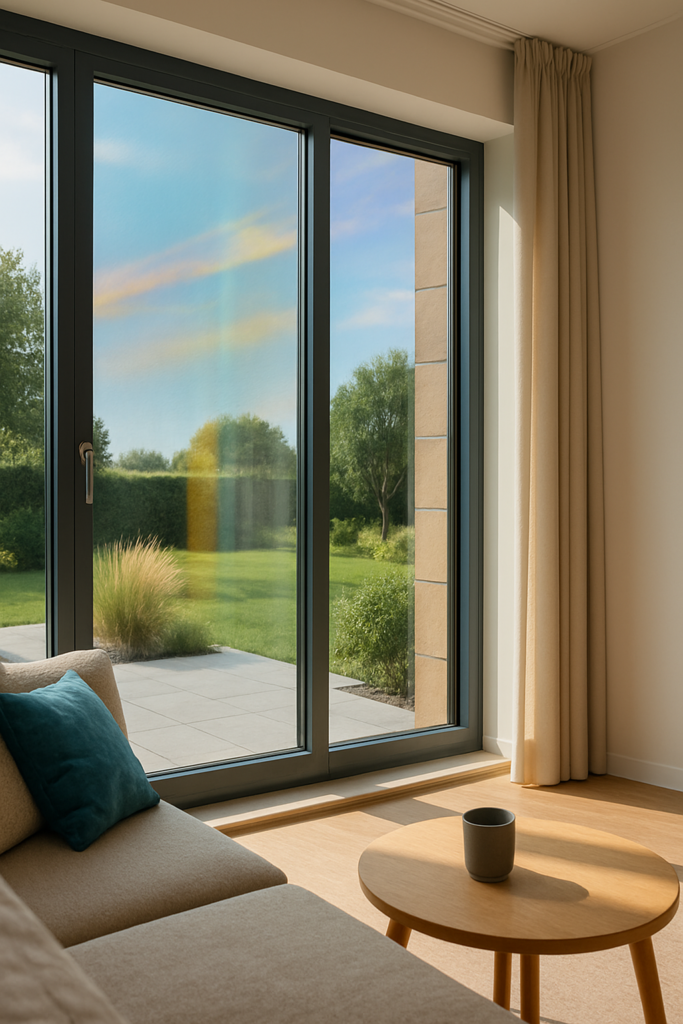
This guide breaks down how low emissivity glass improves comfort in residential homes, from temperature and glare to noise, condensation