When designing modern buildings, one of the most important factors to evaluate is the energy efficiency of glazing systems. For architects and engineers seeking both performance and safety, SGP laminated glass has become a preferred solution. One crucial metric in determining its thermal performance is the U-value.
In this article, we break down what U-value means, how SGP laminated glass performs thermally, and why it’s essential for high-performance windows, facades, and skylights. We also explore how to optimize U-value with coatings, interlayers, and insulated units.
What Is U-Value in Glazing?
U-value measures how well a building material—like a window or glass panel—prevents heat from escaping. It’s expressed in W/m²·K (watts per square meter per Kelvin). The lower the U-value, the better the material insulates.
For glass, U-value depends on:
- Number of panes
- Glass thickness
- Type of interlayer
- Gas fill between panes (e.g., argon)
- Coatings like low-emissivity (Low-E)
Standard single-pane glass has a U-value of around 5.8 W/m²·K, while high-performance glazing can achieve values below 1.0 W/m²·K.
What Is SGP Laminated Glass?
SGP laminated glass uses SentryGlas® Plus, an ionoplast interlayer that provides:
- Enhanced structural integrity
- Impact resistance
- Moisture resistance
- Long-lasting optical clarity
Unlike standard laminated glass that typically uses PVB, SGP laminated glass is five times stronger and 100 times stiffer, making it ideal for frameless windows, curtain walls, and glass canopies.
Learn about its structural capabilities:
🔗 SGP Laminated Glass for High-Performance Window Systems
SGP Laminated Glass and U-Value
While the SGP interlayer does not directly reduce the U-value as much as low-E coatings or gas fills, it plays a supportive role in high-performance window systems when used in conjunction with:
- Insulating glass units (IGUs)
- Low-E coatings on one or more surfaces
- Double or triple glazing
- Edge spacers and thermal breaks
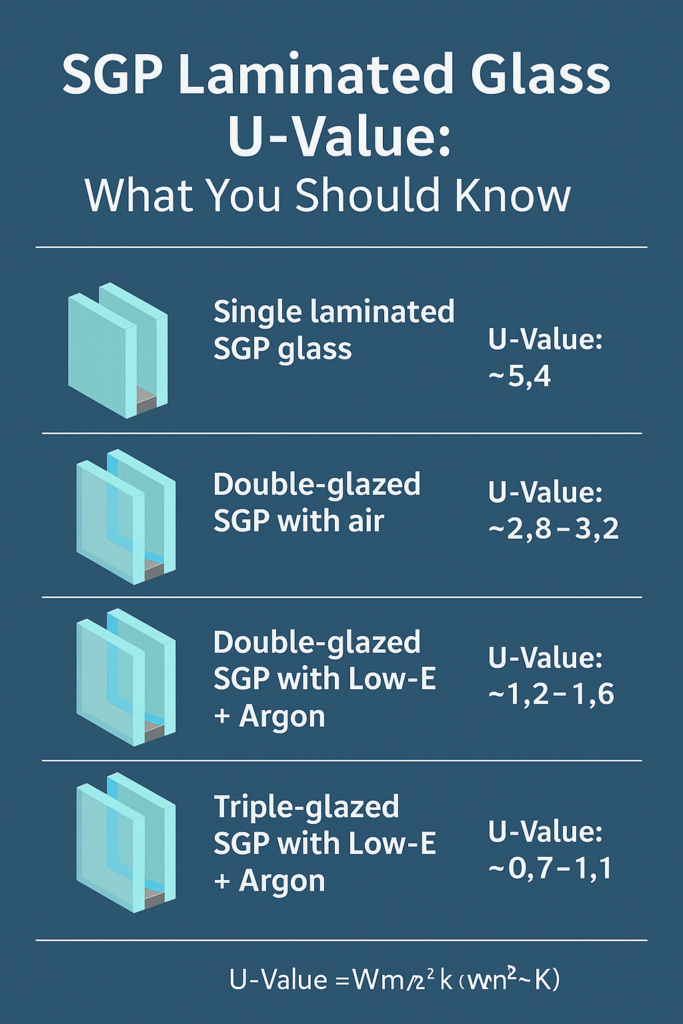
Typical U-Values with SGP Laminated Glass
| Configuration | Estimated U-Value (W/m²·K) |
|---|---|
| Single laminated SGP glass (6.76mm) | ~5.4 |
| Double-glazed with SGP laminated + air | ~2.8–3.2 |
| Double-glazed with SGP + Low-E + Argon | ~1.2–1.6 |
| Triple-glazed SGP + Low-E + Argon | ~0.7–1.1 |
U-value is improved significantly when SGP laminated glass is used in an insulated glass unit with gas fill and coatings.
Energy Efficiency with SGP Laminated Glass
1. Heat Retention in Winter
Using laminated glass with Low-E coatings and insulating layers reflects radiant heat back into the building, maintaining interior warmth and reducing heating costs.
2. Solar Heat Control in Summer
SGP laminated glass combined with solar control coatings helps reduce heat buildup in summer, lowering cooling loads and improving comfort.
3. UV Protection
SGP laminated glass blocks over 99% of UV rays, protecting interiors from fading and reducing unwanted solar heat gain.
These characteristics make SGP ideal for:
- Passive house projects
- Energy-efficient curtain walls
- Floor-to-ceiling residential glazing
SGP Laminated Glass in Design and Architecture
Because of its clarity and minimal need for edge framing, SGP laminated glass in design supports:
- Panoramic windows
- Structural glass walls
- Frameless balustrades
- Glass staircases and facades
With superior thermal and structural performance, SGP offers durability in both residential and commercial builds.
Discover more architectural benefits here:
🔗 SGP Laminated Glass
SGP Laminated Glass Installation Considerations
To achieve the best U-value performance, SGP laminated glass should be installed:
- As part of an IGU with argon or krypton fill
- Using thermally broken frames
- With edge spacers that reduce thermal bridging
- With internal Low-E coatings to reflect IR energy
SGP laminated glass installation should always be handled by experienced glazing professionals to ensure airtightness and long-term thermal integrity.
SGP Laminated Glass Care and Maintenance
To maintain performance and clarity:
- Use pH-neutral cleaners
- Avoid abrasive tools or harsh chemicals
- Clean drainage and edge seals to prevent water pooling
- Inspect for fogging or condensation in IGUs
With minimal SGP laminated glass maintenance, systems can last over 30–50 years.
Price of SGP Laminated Glass for Energy-Efficient Builds
| Glass Type | Price Range (USD/m²) |
|---|---|
| SGP Laminated (clear, 13.52mm) | $100–$180 |
| SGP + Low-E + Argon Double Glazed Unit | $160–$240 |
| Triple IGU with SGP + Low-E + Krypton | $240–$320+ |
Factors influencing SGP laminated glass price include thickness, coatings, interlayer configuration, and custom shapes.
Who Manufactures High-Performance SGP Laminated Glass?
When selecting a supplier, look for:
- Verified SGP laminated glass manufacturers
- Energy rating certifications
- Cut-to-size and insulated unit services
- Thermal and acoustic performance data
Partnering with experts ensures your glass is fabricated and delivered for maximum energy savings.
Conclusion
SGP laminated glass is more than just a safety or structural component—when used in insulated units with proper coatings, it becomes a powerful contributor to a building’s energy efficiency. Its role in reducing U-values, increasing thermal stability, and improving long-term durability makes it essential for future-ready architecture.
From eco-conscious residences to high-performance commercial facades, understanding the U-value implications of SGP laminated glass can help you design for beauty, strength, and sustainability.
Discover how to integrate SGP into your energy-efficient plans:
🔗 SGP Laminated Glass for High-Performance Window Systems
🔗 SGP Laminated Glass
🔗 SGP vs PVB Laminated Glass