In an age where glass plays a structural and aesthetic role in modern buildings, selecting the right type of glazing is more critical than ever. Whether you’re designing skyscrapers, storefronts, or glass railings, impact resistance is a key safety concern. This is where SGP laminated glass stands out.
Short for SentryGlas® Plus, SGP is a high-performance interlayer used in laminated glass applications where traditional materials like PVB may fall short. Engineered to maintain integrity under pressure, SGP laminated glass handles impacts better—before and after breakage.
This article breaks down the science, structure, and real-world advantages of SGP laminated glass in impact-prone environments, proving why it’s the clear choice for durable, modern architecture.
What Is SGP Laminated Glass?
SGP laminated glass consists of two or more panes of glass bonded by a tough, ionoplast interlayer. Compared to standard PVB-laminated glass, SGP provides:
- 5x more tear strength
- 100x more stiffness
- Better resistance to UV, moisture, and temperature changes
- Superior edge stability
- Exceptional post-breakage load retention
Because of these properties, it’s now the gold standard for structural and safety glazing applications where impact resistance is critical.
For a broad benefits overview:
🔗 5 Reasons SGP Laminated Glass Is Best for Safety and Clarity
How SGP Laminated Glass Handles Impact Differently
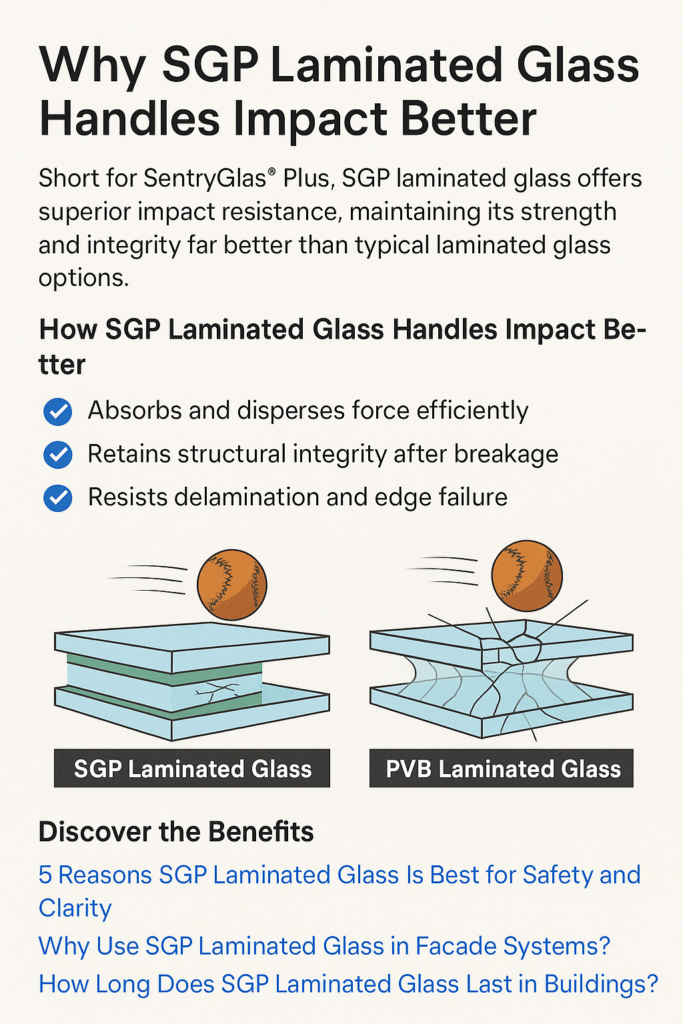
1. Absorbs and Disperses Force More Efficiently
The ionoplast interlayer in SGP is not only stiffer than PVB but also significantly more elastic in the right direction. When an impact occurs (e.g., flying debris, human force, seismic motion), the interlayer:
- Absorbs shock energy
- Prevents penetration
- Disperses the load evenly across the surface
This makes it ideal for:
- Hurricane-rated glass panels
- Glass doors in public buildings
- Skylights and overhead glazing
- Balustrades and railing systems
2. Retains Structural Integrity After Breakage
One of the most significant differences between PVB and SGP laminated glass is how each performs after breaking. SGP:
- Keeps broken pieces adhered to the interlayer
- Maintains panel rigidity
- Continues to support wind or load pressure
- Prevents dangerous sagging or collapse
This level of impact resistance is critical for:
- High-rise facade systems
- Walkable glass floors
- Public safety barriers
Want to know where it performs best?
🔗 Why Use SGP Laminated Glass in Facade Systems?
3. Resists Delamination and Edge Failure
A common issue with traditional laminated glass is delamination after impact or environmental stress. This occurs when the interlayer starts to separate from the glass due to:
- Water ingress
- UV exposure
- Poor installation
SGP’s advanced composition resists:
- Edge clouding
- Yellowing
- Adhesive failure
Even in frameless installations or open-edge conditions, SGP laminated glass maintains integrity and impact performance.
4. Approved for Blast and Ballistic Applications
SGP laminated glass has passed rigorous testing standards for impact and blast resistance, including:
- ASTM E1300 for structural load
- EN 356 for security glazing
- GSA/DoD blast performance
- ISO 16933 for explosion pressure
This makes it suitable for:
- Government facilities
- Airports and transportation hubs
- Commercial buildings in high-risk zones
- Retail centers requiring vandal-resistance
5. Performs in Extreme Environmental Conditions
Impact resistance isn’t just about blunt force—it also includes prolonged exposure to:
- High humidity
- Salt spray (coastal regions)
- Freezing and thawing cycles
- Intense solar radiation
SGP laminated glass retains its strength and clarity where other interlayers fail, making it ideal for:
- Marine applications
- Rooftop glazing
- Outdoor frameless panels
Want to see how long it lasts?
🔗 How Long Does SGP Laminated Glass Last in Buildings?
Common Impact-Resistant Applications Using SGP
- Balcony enclosures in high-rise residential buildings
- Curtain wall systems in hurricane zones
- Railings and staircases in commercial complexes
- Glass bridges and floors with public foot traffic
- Facade elements near pedestrian walkways or street fronts
- Storefronts and skylights in urban high-risk areas
Comparison: SGP vs PVB Under Impact
| Property | SGP Laminated Glass | PVB Laminated Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Impact absorption | Excellent | Moderate |
| Tear resistance | 5x stronger | Weaker under point stress |
| Post-breakage support | Maintains panel shape | Sagging or collapse possible |
| Delamination resistance | High (even in open-edge setups) | Poor in exposed environments |
| Blast/ballistic rating | Certified for high-security use | Limited use |
| UV/moisture resistance | Exceptional | Prone to yellowing and fogging |
Installation Notes for Optimal Impact Performance
Proper sgp laminated glass installation ensures maximum impact resistance. Best practices include:
- Using approved sealants for UV stability
- Providing adequate drainage in edge systems
- Avoiding sharp mechanical loads at corners
- Partnering with certified sgp laminated glass manufacturers
Post-installation care is minimal but crucial for sustained performance.
Conclusion
When it comes to protecting people and property from accidents, weather, or intentional force, SGP laminated glass sets the standard for impact resistance. Its advanced interlayer, edge durability, and post-breakage integrity make it ideal for modern building envelopes where both safety and aesthetics matter.
Whether you’re constructing a glass canopy, a curved atrium, or a transparent floor, SGP laminated glass ensures peace of mind and architectural freedom.
Continue learning about high-performance glass systems:
🔗 5 Reasons SGP Laminated Glass Is Best for Safety and Clarity
🔗 Why Use SGP Laminated Glass in Facade Systems?
🔗 How Long Does SGP Laminated Glass Last in Buildings?